01. 중복 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
@Repository
public class UserRepository{
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager;
public User find(String email) {
return em.find(User.class, email);
}
public void save(User user) {
em.persist(user);
}
//...
}
@Repository
public class HotelRepository{
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager;
public Hotel find(String id) {
return em.find(Hotel.class, id);
}
public void save(Hotel hotel) {
em.persist(hotel);
}
//...
}
UserRepository와 HotelRepository는 다루는 엔티티만 다를 뿐 EntityManager를 이용해서 엔티티를 찾고, 저장하는 코드는 온전히 동일한 구조를 갖는다.
이런 중복 코드 작업을 없앨 수 있는 좋은 방법이 있는데, 그것이 바로 스프링 데이터 JPA를 사용하는 것이다.
02. 스프링 데이터 JPA 소개
스프링 데이터 JPA를 이용해서 많은 중복 코드 작성을 줄일 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public interface UserRepositoty extends Repository<User, String> {
User findOne(String email);
User save(User user);
void delete(User user);
@Query("select u from User u order by u.name")
List<User> findAll();
}
Repository는 스프링 데이터 JPA가 제공하는 인터페이스이다. 이 인터페이스만 상속받아 정해진 규칙에 맞게 메서드를 작성하면 된다. 따라서 EntityManager를 이용한 코드를 중복해서 구현할 필요가 없다.
스프링 데이터 JPA는 Repository를 상속한 인터페이스를 검색하고, 그 인터페이스를 알맞게 구현한 객체를 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//UserRepositoty를 사용할 코드는 다음 처럼 의존성 주입을 통해 UserRepositoty 빈을 주입받아 사용한다.
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
public void setUserRepositoty(UserRepositoty userRepositoty) {
this.userRepositoty = userRepositoty;
}
}
03. 스프링 데이터 JPA 설정
스프링 데이터 JPA를 사용하려면 프로젝트에 spring-data-jpa 모듈에 대한 의존을 추가하면 된다. (369~372p)
04. 리포지토리 인터페이스 메서드 작성 규칙
4-1. 리포지토리 인터페이스 작성
스프링 데이터 JPA를 위한 리포지토리 인터페이스를 작성하는 것이 첫 번째다. 스프링 데이터 JPA는 spring-data-jpa, spring-data-common 모듈을 사용하는데 이 두 모듈이 제공하는 리포지토리 타입 중 하나를 상속받은 인터페이스를 작성하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//T는 엔티티 타입을 의미하고, ID는 식별자 타입을 의미한다.
public interface Repository<T, ID extends Serializable> {
}
public interface UserRepositoty extends Repository<User, String> {...}
//Repository 인터페이스를 상속 받는 대신 애노테이션을 사용해도 된다.
@RepositoryDefinition(domainClass=Hotel.class, idClass = String.class)
public interface HotelRepository {...}
4-2. 기본 메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public interface UserRepository extends Repository<User, String> {
//식별자를 인자로 받는다.
User findOne(String email);
//save 메서드는 해당 엔티티의 상태에 따라 persist()나 merge()를 사용해서 엔티티를 저장한다.
User save(User user);
void delete(User user);
}
스프링 데이터 JPA는 새로운 엔티티인지 여부를 판단할 때 다음과 같은 규칙을 사용한다.
- 해당 엔티티 클래스가 Persistable 인터페이스를 구현했다면 isNew() 메서드로 새로운 엔티티인지 검사한다.
- 엔티티에 @Version 속성이 있다면 버전 속성이 null인 경우 새 엔티티로 간주한다.
- 식별자가 기본 데이터 타입이 아니면 식별자가 null인 경우 새 엔티티로 간주한다. 숫자 타입이면 값이 0인 경우 새 엔티티로 간주힌디.
4-3. 조회 메서드 기본 규칙
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public interface UserRepository {
// 모든 엔티티 조회 - List, Iterator, Collection 타입을 사용해도 된다.
List<User> findAll();
// 특정 속성을 이용해서 엔티티 검색 - findBy속성
List<User> findByEmail(String email);
// And 조건을 이용해서 두 개 이상의 속성에 대한 비교 연산을 조합할 수 있다.
List<User> findByEmailAndName(String email, String name);
// 속성명 뒤에 비교 연산자를 위한 키워드 추가도 가능하다. 예) 지정한 날짜 이후인지 비교
List<User> findByCreateDateAfter(Date date);
}
public interface HotelRepository {
// 중첩 프로퍼티를 지정할 수도 있다. where h.address.zipcode = ?
List<Hotle> findByAddressZipcode(String zipcode);
}
스프링 데이터 JPA는 메서드 이름을 대문자 기준으로 구성 요소를 판단한다. find(select), By 절은 where 조건이 시작됨을 뜻함, By 키워드 뒤에 오는 속성은 엔티티의 속성을 뜻한다.
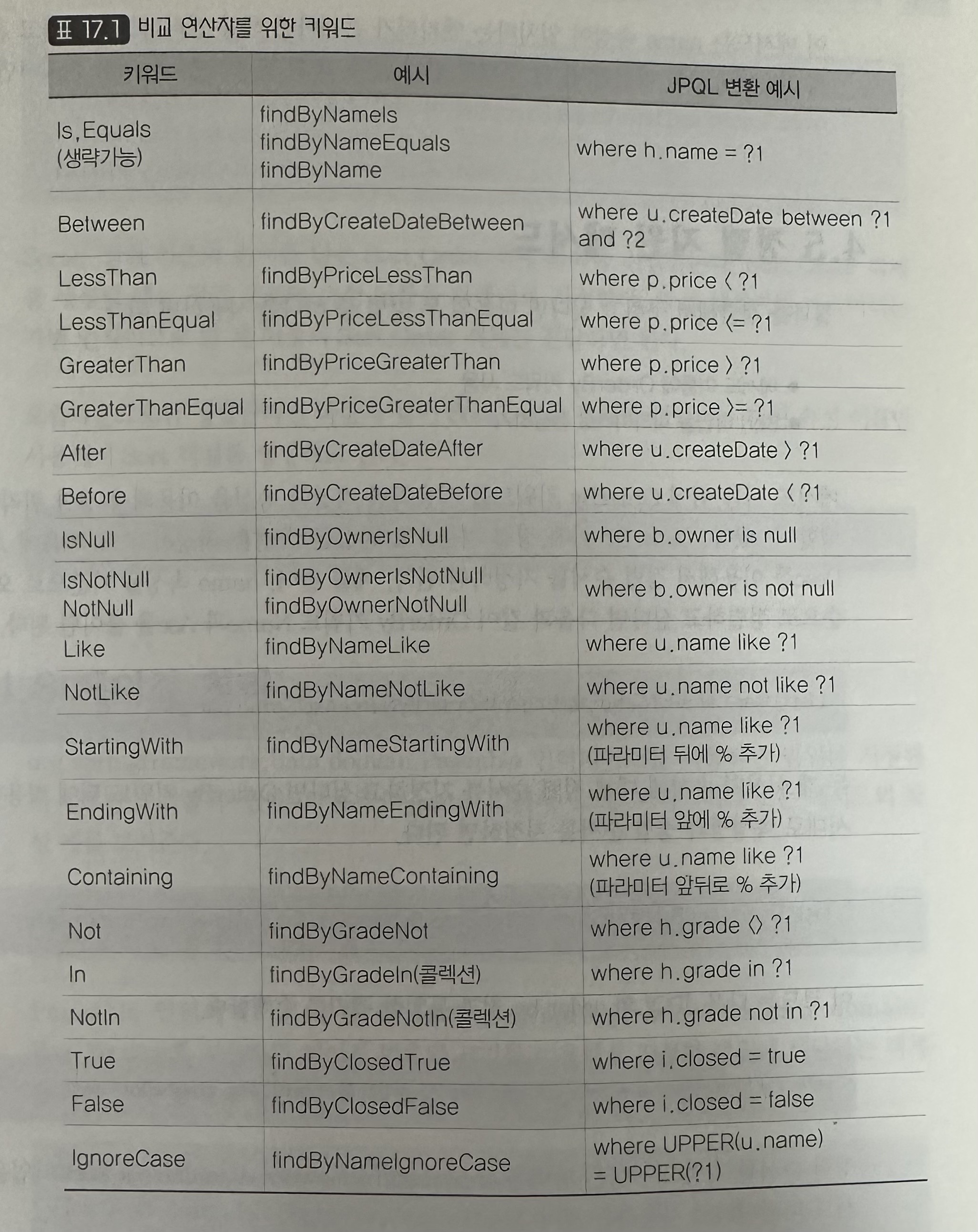
4-4. 힌 개 결과 조회
단일 결과를 조회하고 싶다면 콜렉션 대신 조회 타입을 리턴 타입으로 사용하면 된다.
1
User findByName(String name);
4-5. 정렬 지원 메서드
정렬을 하기 위한 방버으로는
- 메서드 이름에 OrderBy 키워드 사용
- Sort 타입을 파라미터로 전달하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
List<User> findByNameStartingWithOrderByNameAsc(String name);
List<User> findAll(Sort sort);
Sort sort = new Sort(
new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC, "name"),
new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "createDate")
);
List<User> users = userRepository.findAll(sort);
4-6 페이징 처리
Pageable 인터페이스를 사용하면 범위를 지정해서 일부만 조회할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
List<User> findByNameStartingWith(String name, Pageable pageable);
PageRequest pageRequest = new PageRequest(0, 10);
List<User> user = userRepository.findByNameStartingWith("최", pageRequest);
Sort sort = new Sort("name");
PageRequest pageRequest = new PageRequest(1, 10, sort);
List<User> users = userRepository.findByNameStartingWith("최", pageRequest);
리턴타입으로 Page를 사용할 수도 있다. Page 인터페이스는 다음과 같은 메서드를 제공한다.
- int getTotalPages() - 전체 페이지 개수
- long getTotalElements() - 전체 개수
- int getNumber() - 현재 페이지 번호
- int getSize() - 한 페이지의 크기
- int getNumberOfElements() - 현재 페이지의 항목 개수
List<T> getContent()- 현재 페이지의 조회 결과- boolean hasContent - 조회 결과가 존재하면 true
- boolean isFirst() - 현재 페이지가 첫 번째이면 true
- boolean isLast() - 현재 페이지가 마지막이면 true
- boolean hasNext() - 다음 페이지가 존재하면 true
- boolean hasPrevious() - 이전 페이지가 존재하면 true
- Sort getSort() - 현재 결과를 구할때 사용한 Sort 객체
- Pageable nextPageable() - 다음 페이지를 구하기 위한 Pageable 객체를 리턴
- Pageable previousPageable() - 이전 페이지를 구하기 위한 Pageable 객체를 리턴
4-7 결과 개수 제한
단순히 첫 번째 결과나 처음 몇 개 결과만 조회하고 싶다면 First 키워드나 Top 키워드를 사용한 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
- findFirst / findTop
- findFirstN / findTopN
4-8. JPQL 사용하기
메서드 이름이 다소 복잡하거나 길다면 실행할 JPQL을 직접 지정할 수도 있다. @Query 애노테이션을 메서드에 적용하고 실행할 JPQL을 지정하면 된다.
05. Specification을 이용한 검색 조건 조합
크리테리아를 사용하면 검색 조건인 Predicate를 조합할 수 있다. 검색 조건을 생성하고, 조합하기 위해서 CriteriaBuilder가 필요한데 이는 EntityManager가 필요하다.
스프링 데이터 JPA는 EntityManager 없이 검색 조건을 조합할 수 있는 기능을 제공하는데 이 기능이 바로 Specification이다. 이것을 사용하기 위한 방법으로는
- 리포지토리 인터페이스에 Specification을 입력받는 메서드를 정의
- 검색 조건을 생성하는 Specification을 구현하기
- 검색 조건을 조합한 Specification을 객체로 검색하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Paga<Hotel> findAll(Specification<Hotel> spec, Pageable pageable);
public class HotelSpecs{
public static Specification<Hotel> bestGrade() {
return new Specification<Hotel>(){
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(
Root<Hotel> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
return cb.equal(root.get("grade"), Grade.STAR7);
}
};
}
public static Specification<Hotel> nameLike(String name) {
return(root, query, cb) -> cb.like(root.get("name"), "%" + name + "%");
}
}
Sort sort = new Sort(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "name"));
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0,3,sort);
//grade 속성이 STAR7dls Hotel을 name 기준으로 내림차순으로 정렬한 결과를 구한다.
Specification<Hotel> bestGradeSpec = HotelSprecs.bestGrade();
Page<Hotel> hotels = hotelRepository.findAll(bestGradeSpec, pageable);
두 조건을 조합하고 싶다면 Specifications (이름 뒤에 s가 붙은)를 사용한다.
1
2
3
Specifications<Hotel> specs = Specifications.where(HotelSpecs.bestGrade());
specs = specs.and(HotelSpecs.nameLike("구로"));
Page<Hotel> hotels = hotelRepository.findAll(specs, pageable);
Specifications 타입은 Specification 타입을 상속받고 있어서 and(), or(), not() 메서드에 Specifications 객체도 전달할 수 있다. and(), or(), not() 메서드는 항상 새로운 Specifications 객체를 생성한다.
검색 조건이 없는 경우에는 빈 Specification을 전달하면 된다.
06. 스프링 데이터가 제공하는 인터페이스 상속받기
findOne, save, findAll과 같은 메서드는 다수의 리포지토리에서 제공하는 메서드이다. 이것은 각 리포지토리 인터페이스에서 동일한 형태의 메서드를 갖게 된다. 스프링 데이터 JPA를 사용하면 구현 코드뿐만 아니라 중복된 메서드마저 작성하지 않아도 된다.
387~390p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public interface HotelRepository extends CrudRepository<Hotel, String> {
//CrudRepository가 이름처럼 저장, 조회, 삭제와 관련된 기본 기능을 제공하므로 필요한 메서드만 정의하면 된다.
}
//PagingAndSortingRepository 인터페이스는 페이징과 정렬 기능을 추가한 메서드를 제공한다.
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
//...
}
//JPA와 관련된 추가 기능을 제공한다.
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
//...
//파라미터로 전달받은 엔티티 객체를 한 쿼리로 삭제
void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);
//모든 엔티티를 조회한 뒤 deleteInBatch()로 삭제하는 방식으로 동작 (잘못 사용하면 성능에 심각한 문제가 발생한다.)
void deleteAllInBatch();
}
//Specification을 사용하는 메서드가 필요하다면 JpaSpecificationExecutor 인터페이스를 사용한다.
public interace JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> {
//...
}
JpaRepository와 JpaSpecificationExecutor의 두 인터페이스를 상속하면 리포지토리에 필요한 대부분의 메서드를 제공하고 있어 findBy와 같이 추가로 필요한 메서드만 작성하면 된다.
