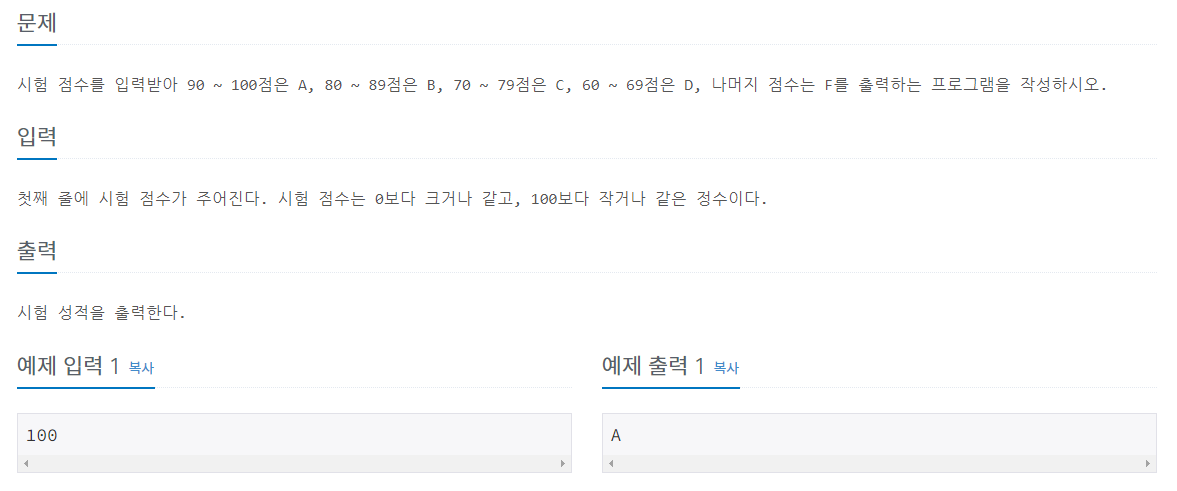
문제
백준에서 단계별로 풀어보기 진행 중 새로 알게된 사실 하나!
1단계에서부터 입력 받은 값으로 결과를 내는 문제가 있었는데 나는 계속 java.util 패키지의 Scanner를 사용하여 문제를 풀었다.
그런데 다른 사람과 결과를 비교했을 때 속도에서 차이가 발생하여 다른 사람의 답지를 보고 새로운 것을 알았다.
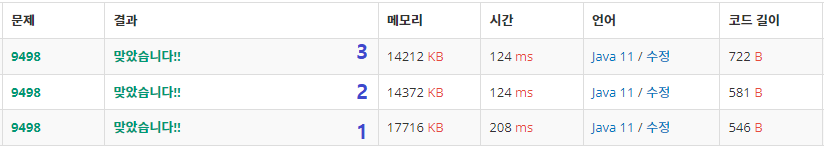
1)Scanner를 사용한 방식 -> 208ms 시간 / 17716KB 메모리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int score = scanner.nextInt();
String result = "";
if(score >= 90 && score <= 100) result = "A";
else if(score >= 80 && score <= 89) result = "B";
else if(score >= 70 && score <= 79) result = "C";
else if(score >= 60 && score <= 69) result = "D";
else result = "F";
System.out.println(result);
scanner.close();
}
}
2)BufferedReader 사용한 방식 -> 124ms시간 / 14372KB 메모리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int score = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String result = "";
if(score >= 90 && score <= 100) result = "A";
else if(score >= 80 && score <= 89) result = "B";
else if(score >= 70 && score <= 79) result = "C";
else if(score >= 60 && score <= 69) result = "D";
else result = "F";
System.out.println(result);
}
}
3)BufferedReader, BufferedWriter 사용한 방식 -> 124ms 시간 / 14212KB 메모리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int score = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String result = "";
if(score >= 90 && score <= 100) result = "A";
else if(score >= 80 && score <= 89) result = "B";
else if(score >= 70 && score <= 79) result = "C";
else if(score >= 60 && score <= 69) result = "D";
else result = "F";
bw.write(result);
bw.flush(); //버퍼에 남아있는 데이터를 출력(비움)
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
BufferedReader / BufferedWriter
버퍼를 이용해서 읽고 쓰는 함수로 버퍼를 이용하기 때문에 입출력의 효율이 비교할 수 없을 정도로 좋아진다. 키보드로 입력한 글자를 버퍼에 하나씩 담아 버퍼가 가득 차거나, 개행 문자가 나타나면 버퍼의 내용을 한 번에 전송한다.
BufferedReader는 Scanner와 유사하나 Scanner는 스페이스, 엔터를 경계로 입력 값을 인식하기 때문에 따로 가공할 필요 없어서 편리하다. 반면 BufferedReader는 엔터만 경계로 인식하고 받은 데이터가 String으로 고정되기 때문에 데이터를 따로 가공해야 하는 경우 번거롭다. 하지만 Scanner에 비해 상대적으로 빠르다.
readLine()를 사용하여 데이터를 라인 단위 로 읽을 수 있으나 리턴 값이 String으로 고정되어 있기 때문에 다른 타입으로 입력 받으려면 형변환을 해주어야 한다. 또한 예외처리를 꼭 해주어야 한다.
라인 단위로 읽은 데이터를 공백 단위로 가공하고자 할 때 다음의 방법을 사용할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// 1) StringTokenizer
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
// String.split() 함수
String arr[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
BufferedWriter는 System.out.println() 과 유사한 것으로 System.out.println()보다 속도가 빠르다.
write() 메서드 를 사용하여 출력할 내용을 담고, flush() 메서드 를 통해 버퍼를 비워내고 동시에 콘솔에 출력한다. 그리고 BufferedWriter도 반드시 예외처리가 필요하다.